▤ 목차
Introduction to Probability and Probability Distributions
In this week, you will learn about the probability of events and various rules of probability to correctly do arithmetic with probabilities. You will learn the concept of conditional probability and the key idea behind Bayes’ theorem. In lesson 2, we generalize the concept of probability of events to a probability distribution over random variables. You will learn about some common probability distributions like the Binomial distribution and the Normal distribution.
Introduction to Probability
What is Probability?
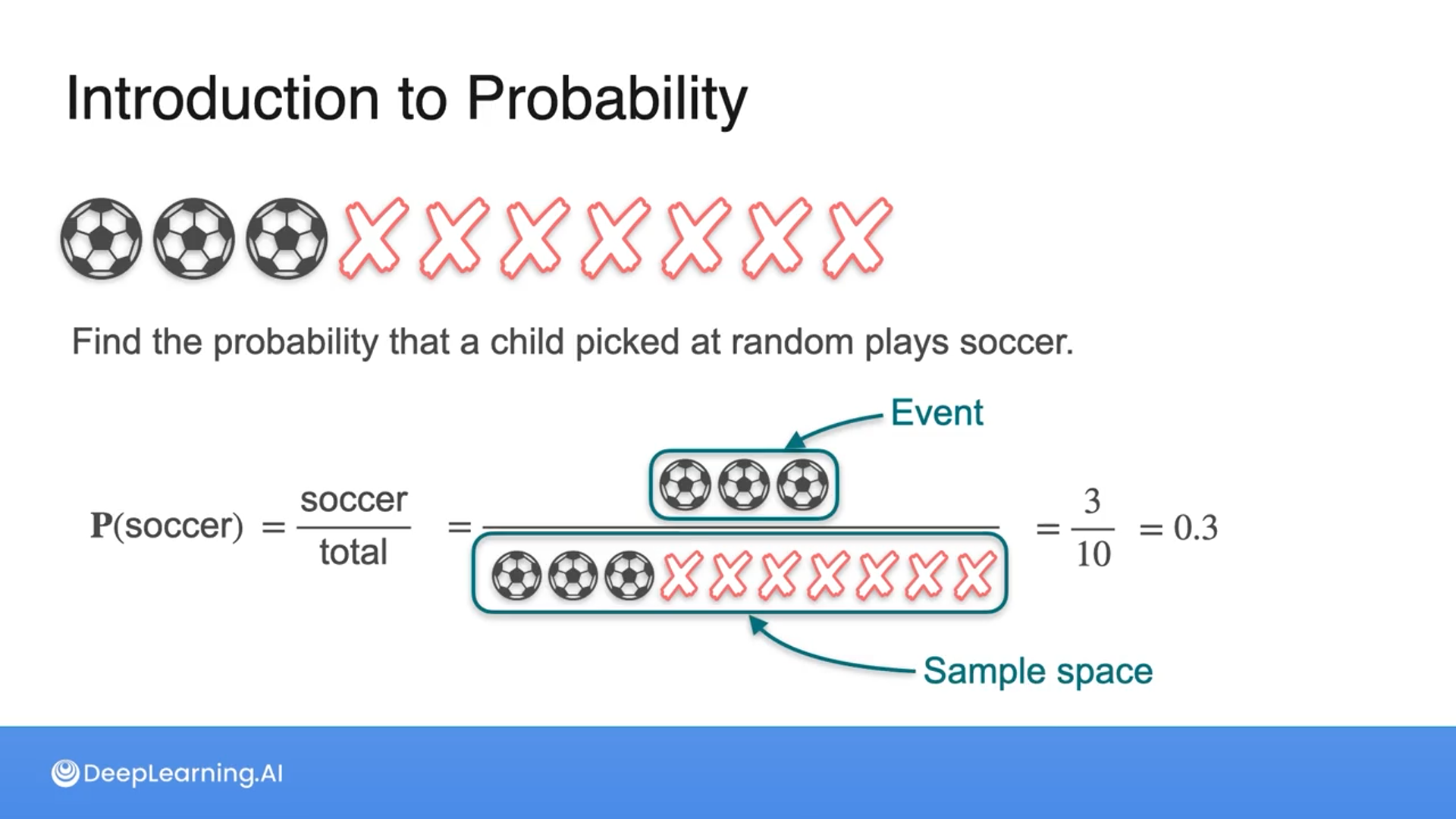
A probability is a measure of how likely an event is to occur.

In a school where there are 10 kids, 3 kids play soccer and 7 kids don't play soccer. What is the probability that a kid picked at random plays soccer?
30%


An experiment is any process that produces an uncertain outcome.

What is the probability of getting two heads when flipping two coins?
1/4
Correct! There are 4 possible outcomes and 'head, head' is only one of them.


What is the probability of a coin landing on heads 3 times?
1/8

What is Probability? - Dice Example
This time, we use dice to get the probabilities.

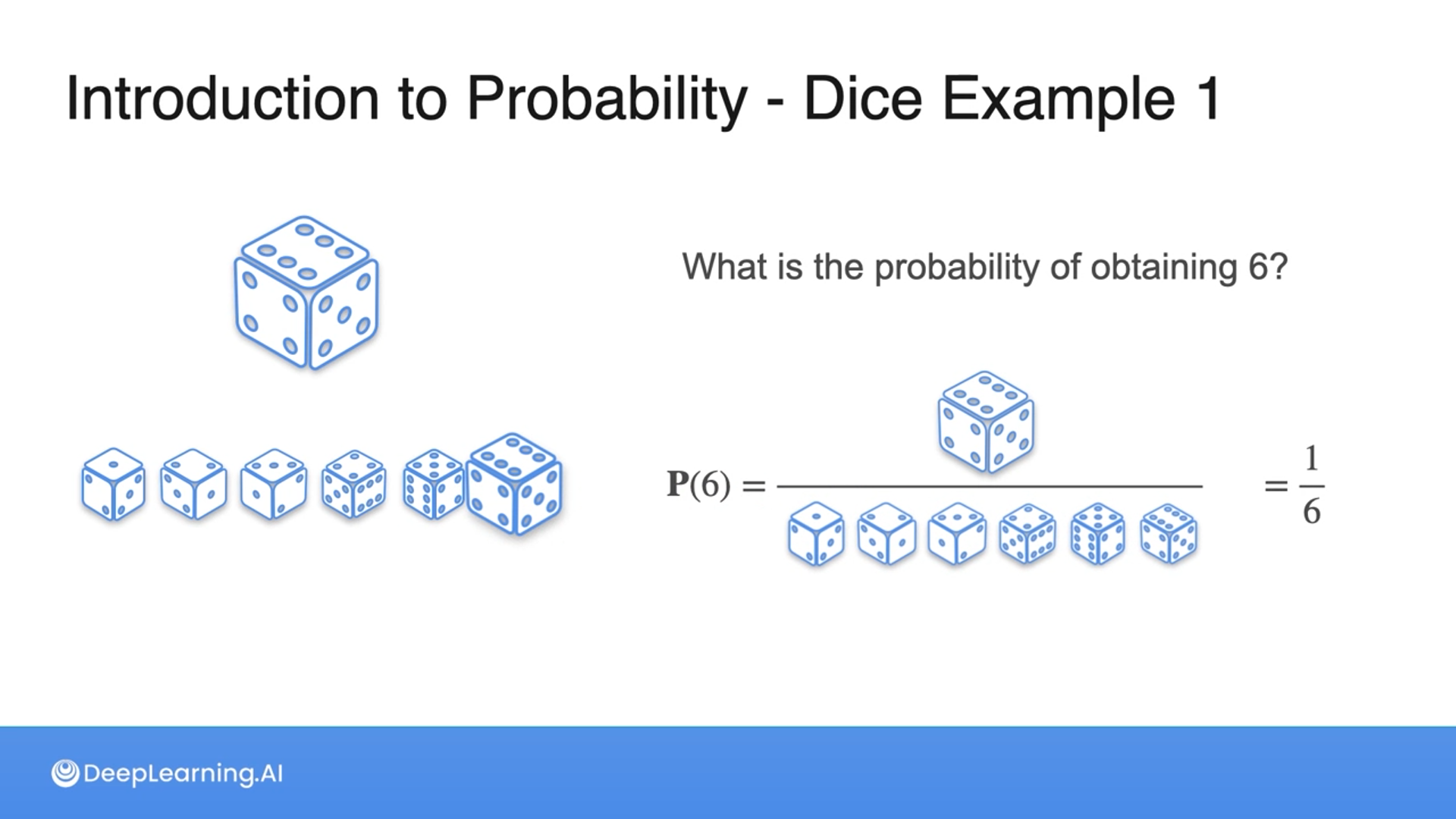
What is the probability of obtaining a 6 when rolling a 6-sided dice?
1/6
Correct! There are 6 equally likely possibilities and 6 is one of them, therefore the probability is 1/6.

When rolling two 6-sided dice, what is the probability of getting 6, 6?
1/36
Correct! Now, there are 6 x 6 = 36 possible outcomes, and (6, 6) is one of them, therefore the probability is 1/36

Complement of Probability
Complement of probability is how likely an event won’t occur.
It's $1 - \text{probability}$.

What is the probability of a child NOT playing soccer?
7/10
Correct! $P(\text{not} \,\,soccer) = {7\over10}$





When flipping a coin three times, what is the probability of not landing on heads 3 times?
Correct! We have that $P(\text{not}\,HHH) = 1-P(HHH) = 1-{1\over8}={7\over8}$


When throwing a 6-sided dice, what is the probability of obtaining anything other than 6?
5/6

All the information provided is based on the Probability & Statistics for Machine Learning & Data Science | Coursera from DeepLearning.AI
'Coursera > Mathematics for ML and Data Science' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Probability & Statistics for Machine Learning & Data Science (3) (2) | 2024.09.05 |
|---|---|
| Probability & Statistics for Machine Learning & Data Science (2) (0) | 2024.09.04 |
| Probability & Statistics for Machine Learning & Data Science (0) (0) | 2024.09.02 |
| Calculus for Machine Learning and Data Science (11) (3) | 2024.09.01 |
| Calculus for Machine Learning and Data Science (10) (3) | 2024.08.31 |




 }
}